Proofpoint’s 2022 Cost of Insider Threats Global Report revealed that on average, impacted organizations spent $15.4 million annually on overall insider threat remediation and take 85 days to contain each incident.
Conducted by the Ponemon Institute, the report reveals that over the last two years, the frequency and costs associated with insider threats have increased dramatically across all three insider threat categories, including careless or negligent employees/contractors, criminal or malicious insiders, and cybercriminal credential theft.
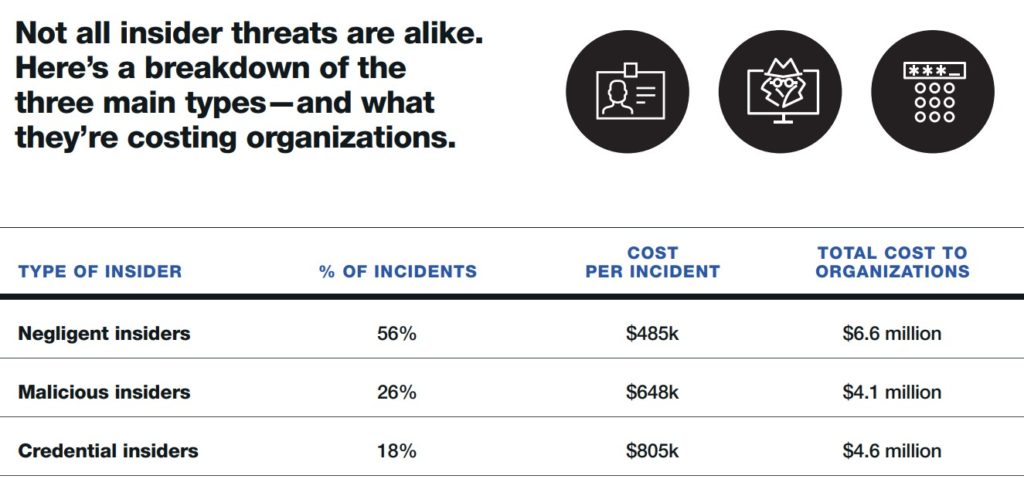
Source: Ponemon Institute, Proofpoint

According to Ryan Kalember, executive vice president of cybersecurity strategy at Proofpoint, months of sustained remote and hybrid work has resulted in an increased risk around insider threat incidents, as people leave organizations and take data with them.
He commented that organizational insiders, including employees, contractors, and third-party vendors, are an attractive attack vector for cybercriminals due to their far-reaching access to critical systems, data, and infrastructure.
“With people now the new perimeter, we recommend layered defences, including a dedicated insider threat management solution and strong security awareness training, to provide the best protection against these types of risks,” he continued.
ASEAN Perspective

Proofpoint's senior director for its advanced technologies group in Asia-Pacific & Japan, Steve Moros, added that the cost and number of insider led cyber security incidents has soared over the last two years with a 34% increase in costs and a total average annual cost of US$15.4M - a 44% increase in numbers with a total of 6,803 Incidents globally.
Moros listed three key contributing factors behind the sharp increase in the ASEAN region:
- How quickly organisations needed to pivot to a work-from-anywhere world with more users accessing business data remotely and from any device.
- The great resignation as people leave organisations and take data with them in some cases by accident, but in many cases they are doing this consciously.
- Organisational insiders, including employees, contractors, and third-party vendors, are an attractive attack vector for cybercriminals due to their access to critical systems and data.
ASEAN CISOs need to focus on the various threat vectors attackers may use.
"Attackers don’t hack in, they log in and with people now the new perimeter, we recommend implementing layered defences that are built from the ground up as people-centric platforms, including a dedicated insider threat management (ITM) solution and strong security awareness training, to provide the best protection against these types of risks," continued Moros.
He also stressed the importance of monitoring who has access to sensitive information and how data moves. "In addition, organisations need to ensure all third-party partners and vendors they do business with are adhering to their cybersecurity guidelines and take the necessary steps to minimise their exposure and risks," concluded Moros.
Report findings summary

Source: Ponemon Institute, Proofpoint
Rising numbers. The overall number of incidents has increased by a staggering 44% in just two years. The frequency of incidents per company has also gone up with 67% of companies experiencing between 21 and more than 40 incidents per year, up from 60% in 2020.
Root cause. The negligent insider is the root cause of most incidents. About 56% of reported insider threat incidents were the result of a careless employee or contractor, costing on average $484,931 per incident.
This could be the result of a variety of factors, including not ensuring their devices are secured, not following the company’s security policy, or forgetting to patch and upgrade.
The insider threat. Malicious or criminal insiders were behind 1 in 4 incidents (26%) at an average cost per incident of $648,062. Malicious insiders are employees or authorised individuals who use their data access for harmful, unethical, or illegal activities. Because employees are increasingly granted access to more information to enhance productivity in today’s work-from-anywhere workforce, malicious insiders are harder to detect than external attackers or hackers.
Credential theft incidents double. At an average of $804,997 per incident, credential theft is the costliest to remediate. The intent of the credential thief is to steal users’ credentials that will grant them access to critical data and information. A total of an average of 1,247 incidents (or 18%) involved cybercriminals stealing credentials.
Longer time to contain the incident. It takes an average of nearly three months (85 days) to contain an insider incident up from 77 days in the previous study. Incidents that took more than 90 days to contain cost organizations $17.19 million on an annualized basis, while incidents that lasted less than 30 days cost an average of $11.23 million.
Industry landscape. Financial services and professional services have the highest average activity costs. The average activity cost for financial services is $21.25 million and professional services are $18.65 million. Service organizations represent a wide range of companies including accounting, consultancy, and professional service firms
Organizational size affects the cost per incident. The cost of incidents varies according to organizational size. Large organizations with a headcount of more than 75,000 spent an average of $22.68 million over the past year to resolve insider-related incidents. To deal with the consequences of an insider incident, smaller-sized organizations with a headcount below 500 spent an average of $8.13 million.
Five signs that your organization is at risk
- Employees are not trained to fully understand and apply laws, mandates, or regulatory requirements related to their work and that affect the organization’s security.
- Employees are unaware of the steps they should take to ensure that the devices they use—both company issued and BYOD—are always secured.
- Employees are sending highly confidential data to an unsecured location in the cloud, exposing the organization to risk.
- Employees break your organization’s security policies to simplify tasks.
- Employees expose your organization to risk if they do not keep devices and services patched and upgraded to the latest versions.
Dr. Larry Ponemon, chairman and founder of the Ponemon Institute commented: “Insider threats continue to climb, both in frequency and remediation cost. That said, we are seeing the risk of malicious insider threats increase – with more users accessing business data from outside the confines of the office. This can blur the security team’s ability to identify and differentiate between well-meaning employees, and malicious insiders trying to siphon sensitive business data.”




