Juniper Research predicts the total number of patients using RPM (Remote Patient Monitoring) solutions will reach 115.5 million globally by 2027, a 67% growth over the 75 million expected this year.
The substantial growth in market size will be driven by greater pressure on healthcare systems, including clinical staff shortages and limited space within hospitals, driving the need for alternative healthcare solutions.
By 2027, roughly 1.4% of the total population will be turning to RPM, which enables care to be moved outside of overstressed healthcare facilities; thus, boosting healthcare providers’ efficiency. RPM solutions encompass a variety of health monitoring devices which enable continuous communication between patients and healthcare providers, without the need for close contact.
Prevalence of cardiac conditions to drive RPM adoption
By 2027, Juniper Research sees some 90 million cardiac patients using RPM solutions. Given the high global prevalence of cardiac conditions, the firm urged healthcare providers use RPM solutions to monitor the heart rate and blood pressure of cardiac patients at home to lower the number of patients in hospital.
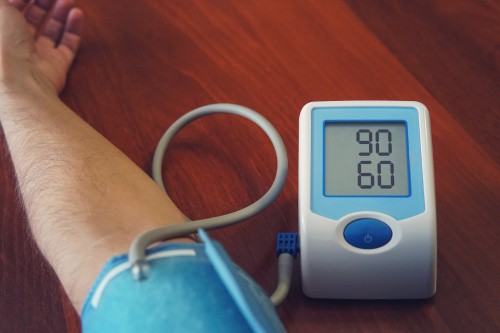
RPM solutions will also indirectly decrease disease transmission rates and alleviate pressure on healthcare systems by reducing the demand for hospital beds.
Research author Cara Malone said: “There are a variety of connected devices that can be used for cardiac patient monitoring, for example blood pressure and heart rate monitors, which can be challenging for less technologically literate patients. Vendors must prioritise device simplification through software improvements, whilst also incorporating patient education to improve healthcare outcomes.”
AI analysis key to real-time data monitoring
Juniper Research also encouraged healthcare service providers to fully leverage the data generated by the increase in adoption of RPM devices.
To maximise the benefits, it recommended that RPM services fully incorporate AI within their solutions to enable healthcare professionals to improve the efficiency of medical triage processes through a predictive proactive healthcare provision model.




