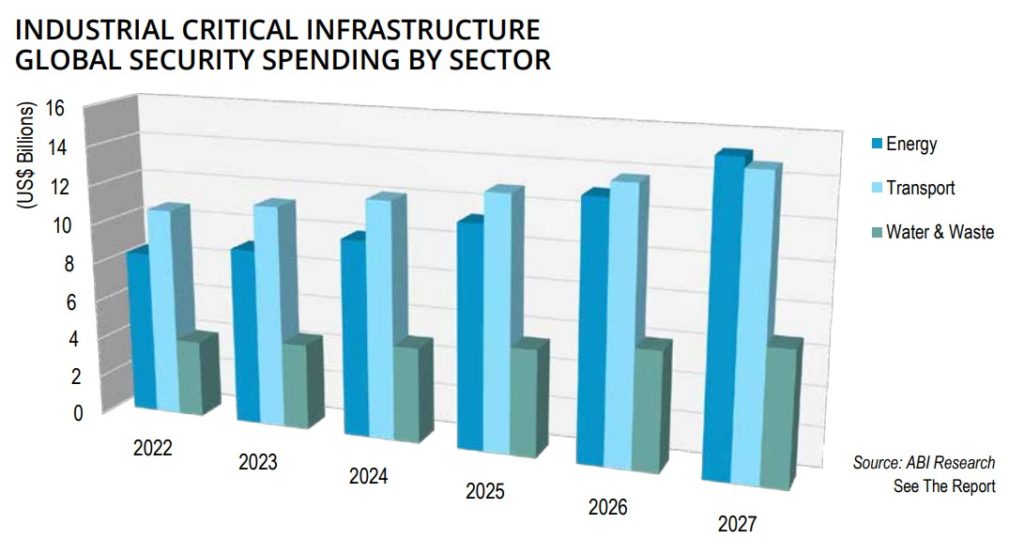
Global cybersecurity spending in industrial critical infrastructure sectors (e.g., energy, transport, and water & waste management) is expected to hit US$23 billion by the end of 2022 and grow at a CAGR of 10% to reach US$36.67 billion in 2027.
Businesses, industries, and in fact the entire world, have never been more connected than they are right now. They have also never been more at risk. According to Michela Menting, digital security research director at ABI Research, organisations and verticals continue to integrate technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G, and blockchain, meaning more points of connection—and points of vulnerability—than ever before.
“As a result, ensuring security is not just a hardware issue or a software issue—it is a web of challenges and solutions spanning entire technology ecosystems,” she concluded.
Citizen digital identity
The growing presence of mobile identities: Driven by digital transformation and governments’ growing appetites to extend digital platform offerings, significant uptake of mobile identities has resulted. Mobile identities, as a companion to physical documentation, once provisioned digitally via a dedicated application or web-based solution, enhance citizen use cases and allow for Identification (ID) verification using no superfluous citizen data.
Cybersecurity applications
The emergence of next-generation cryptography: The concern with quantum-safe technologies is becoming a high priority as the advent of attack-capable quantum computers emerges on the horizon. The imminent release of draft quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms (known as Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC)) by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has security and technology vendors on the starting line, ready to integrate and deploy them in their product lines.
Digital payment technologies
Central banks embracing digital currency: The digitisation of a country’s fiat currency involves the central bank of the economy in question issuing electronic tokens, instead of the usual process of minting coins and printing paper bills. There can be no doubt that recent years have seen the concept of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) explored with great intent by many global economies.
Industrial cybersecurity
Critical infrastructures primed to adopt enabling cybersecurity solutions: Industrial operators are increasingly incorporating disruptive technologies in their migration to Industry 4.0, driving better appreciation of cybersecurity requirements in of enabling technologies with demand for fast user switching, hot patching, ICS cloudification, network probes, and secured PLC programming, among others.
IoT cybersecurity
Optimising data security in telematics to enable intelligence-driven monetisation: Secure data management for automotive telematics is becoming increasingly important for vehicle manufacturers (VMs), Tier One suppliers, telcos and insurance companies. Almost every aspect of the software-defined vehicle is set to include constantly evolving cybersecurity technologies at the hardware, software and network level, with telematics data security being one of the core operations.
Telco cybersecurity
The drive toward embedded cellular connectivity continues: With the hyper-connected world on the horizon, the drive toward embedded cellular connectivity continues, served via Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) form factors, such as eSIM and Integrated SIM (iSIM). From consumer electronics, cutting across a variety of device types from smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearables to myriad Machine-to-Machine (M2M) and IoT applications
Trusted device solutions
The impact of a remote workforce: Distributed working environments affect both workers and assets (IT, OT, and the IoT). Secure connectivity and identity management have become key priorities in disparate and heterogeneous networks. All these elements are driving demand for hardware security.




