Akamai Technologies’ 2022 State of the Internet report indicates a severe risk to the financial services sector in Asia-Pacific and Japan (APJ) region, as attackers ramp up attacks and shift to more sophisticated techniques. Web application and API attacks are increasing at an alarming rate while also growing in complexity.
The new report, Enemy at the Gates, estimate that roughly 80% of cyber attackers additionally aim their efforts at customers of financial services in an attempt to find paths of least resistance for monetary gain.
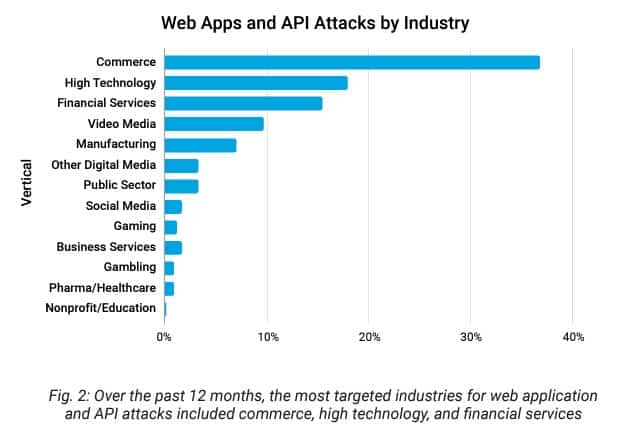
APJ is said to be the most attacked vertical in several critical areas including web application and API attacks, DDoS, phishing, zero-day exploitation, and botnet activities.
APIs as doorways to attack
Most concerning is the surge in web application and API attacks — a 449% growth in the number of attacks against APJ financial services year-over-year.
Akamai claims that web apps and API vectors are commonly used by ransomware groups to gain initial access via the exploitation of vulnerabilities. The surge in web app and API attacks in APJ seems to correlate with the high GDPs of some of the affected countries in the region.
The shortage of cybersecurity skills or talent in the region could potentially be a factor in the increasing number of successful cyberattacks.
Knowing what the attackers are focusing on could help organisations and security practitioners in APJ have a better understanding of their risk exposures and prioritise securing potential weaknesses.
Beyond APIs – other vulnerabilities
The growing number of attacks and increased sophistication coincides with an increasing number of cyberattacks in the region, primarily resulting in ransomware. Previous findings connect web app and API attacks with ransomware.
Australia, Japan, and India are the countries with the highest number of web application and API attacks in the region.
Within 24 hours, exploitation of newly discovered zero-days against financial services reaches multiple thousands of attacks per hour and peaks quickly - affording little time to patch and react.
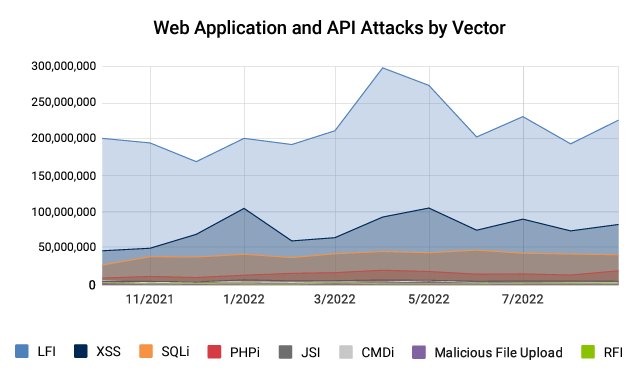
A significant increase in Local File Inclusion (LFI) and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks demonstrates how attackers are shifting toward remote code execution attempts that present a larger strain on internal network security.
Phishing campaigns against financial services customers are introducing techniques that bypass two-factor authentication solutions and increase risk for everyday customers.
Customer account takeover attempts represent over 40% of attack types with another 40% focusing on website scraping, which is used to create more convincing phishing scams.
“Financial services is one of the most attacked industries when new vulnerabilities are discovered, a favourite target of DDoS attacks and continuously focused on by phishing campaigns, which are aimed at their customers who suffer the brunt of these attacks,” said Steve Winterfeld, advisory CISO for Akamai.

“Attackers will always find ways to infiltrate your network or impact your customers. Understanding attack surfaces could provide insights into key risks and therefore allow organisations to devise security controls and mitigation plans to better protect customers.”
Steve Winterfeld





