According to Gartner, the four pillars driving technology innovation across customer service and support (CSS) organisations are getting connected, process orchestration, knowledge and insight, and resource management.
The Gartner Hype Cycle for CSS Technologies, 2022 contains the most-important maturing technologies for supporting customers (see Figure 1).
The Gartner Hype Cycle provides a view of how a technology or application will evolve over time, providing a source of insight to manage its deployment within the context of a specific business goal. It allows clients to get educated about the promise of an emerging technology within the context of their industry and an individual appetite for risk.

“Efforts to increase the use of digital channels and improve automation rates using analytics are driving customer service technology spending, despite economic headwinds,” said Drew Kraus, VP Analyst at Gartner.
“The technologies on this year’s Hype Cycle aim to enhance customer service, create a more seamless customer journey, and better design and direct future journeys.”
Drew Kraus
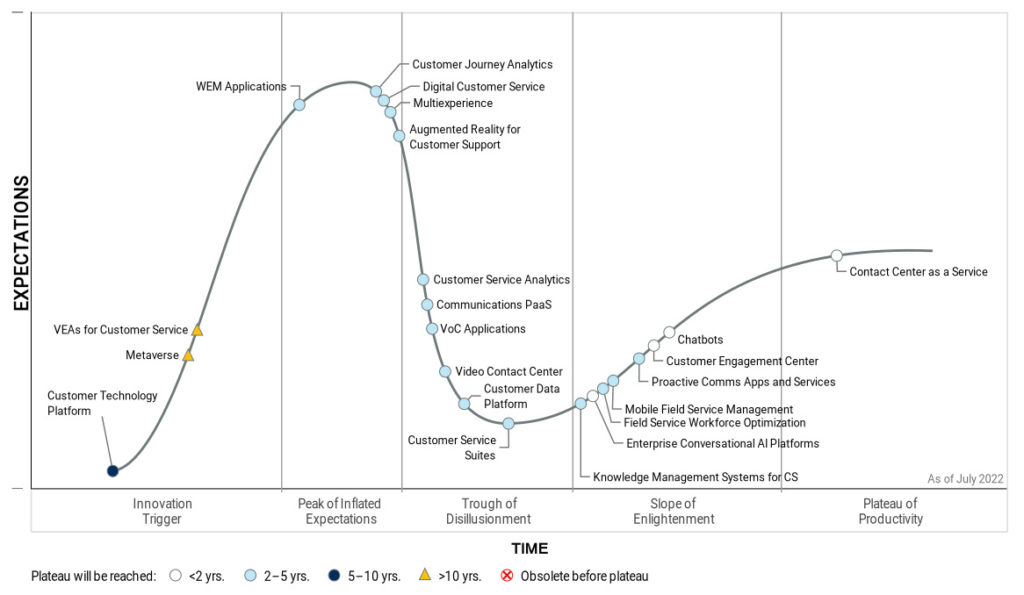
Source: Gartner (August 2022)
Getting connected
This category of technology focuses on delivering a channel-agnostic, architected design to create customer service journeys, including intelligent self-service.
For example, a cloud contact centre as a service (CCaaS) is a cloud-based application service platform that enables organisations to manage multichannel customer interactions holistically with pre-packaged applications to support customers and employee engagement. Creating a seamless customer journey across assisted and self-service channels is the top priority for customer service leaders in 2022 and accelerating CCaaS adoption furthers this endeavour.
“Cloud enables organisations to focus on transforming customer experience (CX), rather than managing the day-to-day technology needs of users, which is fuelling the 22% CCaaS market growth to $10.9 billion in 2023,” said Kraus.
Additional technologies on the Hype Cycle within this category include augmented reality for customer support, consumer messaging applications, proactive communications applications and services, and video contact centres.
Process orchestration
The technologies within the process orchestration pillar support increasingly complex and personalized customer engagements, often via automation. For example, chatbots, a form of virtual customer assistants (VCAs), are expected to become the primary customer service channel for a quarter of organisations within five years as they evolve to handle more involved customer requests.
“Automating interactions in the enterprise has a tremendous business impact that cannot be understated,” said Kraus. “The emergence of sophisticated AI voice capabilities has made large-scale call centre automation viable, with huge potential for savings and positive CX.”
Additional process orchestration profiles on the Hype Cycle include customer engagement centre (CEC), customer technology platforms and multi-experience.
Knowledge and insight
Innovations within this category centre around the delivery of customer and operational insights, and the recommendation of the next best actions across all functional groups. Key technologies on the Hype Cycle here include customer service analytics, customer journey analytics, voice-of-the-customer solutions, and knowledge management for customer service.
As making better use of analytics and AI remains a top three priority for CSS leaders in 2022, many of the technologies in this category can help. One example is customer data platforms (CDPs), or software applications that support marketing and CX use cases by unifying a company’s customer data from multiple channels. CDPs optimise the timing and targeting of messages, offers and customer engagement activities, and enable the analysis of individual-level customer behaviour over time.
Resource management
This category consists of technologies that engage and empower employees, resulting in a stronger CX. For example, workforce engagement management (WEM) solutions expand on the already mature workforce optimisation (WFO) market by accommodating complementary technologies – interaction assistance and voice of the employee (VoE) – that help drive employee engagement. They are expected to have a high impact on service organisations within two to five years.
“WEM brings a much-needed additional dimension to the management of contact centre employees,” said Kraus. “The increase in gig and freelance workers is putting pressure on customer service departments to ensure a high perception of employee experience, without which securing their commitment will be increasingly challenging.”
Other technologies on the Hype Cycle within this pillar include mobile field service management and field service workforce optimisation.




