Veracode’s 2025 GenAI Code Security Report reveals the dangers of vibe coding, where developers rely on AI to generate code, usually without defining security requirements.
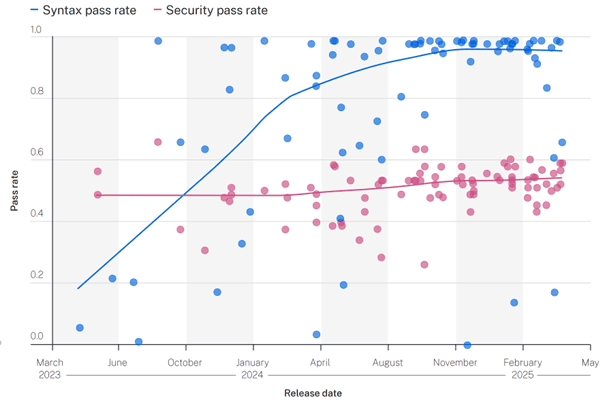
The report, which meticulously analysed 80 curated coding tasks across more than 100 large language models (LLMs), uncovered critical security flaws in AI-generated code. These flaws were found to introduce security vulnerabilities in a staggering 45% of cases.

“Our research reveals GenAI models make the wrong choices nearly half the time, and it’s not improving,” Jens Wessling, chief technology officer at Veracode, said.
Alarmingly, the report noted that AI can enable attackers to identify and exploit security vulnerabilities more quickly and effectively, increasing vulnerabilities and easing exploitation.
Risky code generation languages
The report found that Java is the riskiest language for AI code generation, with a security failure rate over 70%. Python, C#, and JavaScript logged failure rates between 38% and 45%.
According to the research, LLMs failed to secure code against cross-site scripting (CWE-80) and log injection (CWE-117) in 86% and 88% of cases, respectively.
“We found larger models do not perform significantly better than smaller models, suggesting this is a systemic issue rather than an LLM scaling problem,” said Wessling.
Managing application risks
Veracode urges organisations to take a proactive stance in ensuring security as they leverage GenAI development practices, such as vibe coding, in their workflows.
“AI coding assistants and agentic workflows represent the future of software development, and they will continue to evolve at a rapid pace,” Wessling concluded.
“The challenge facing every organisation is ensuring security evolves alongside these new capabilities. Security cannot be an afterthought if we want to prevent the accumulation of massive security debt.”




